This project is funded by the Croatian Science Foundation.
Development of novel antibodies (biologics) that will selectively inhibit hepcidin expression in the liver for the Treatment of Anemia of Chronic Disease
(BMP6Fe3)
Research Project
In this project, we will focus on understanding specified features of BMP6 biology on regulation of serum iron to develop a novel therapy for anemia of chronic disease (ACD), an unmet medical need.
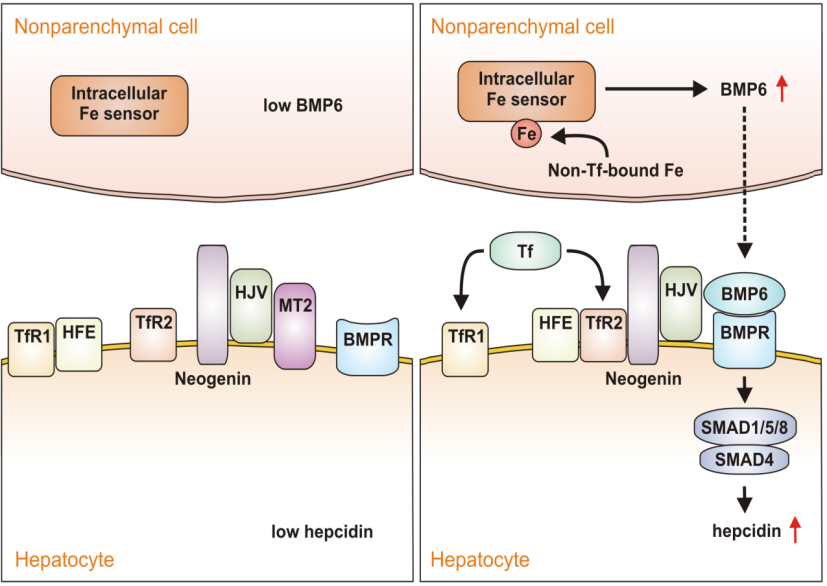
Figure 1. Schematic representation of hepcidin expression in hepatocytes in response to iron levels. Hepcidin expression in hepatocytes is controlled by BMP6 signaling cascade, HJV, neogenin, TfR2 and HFE. Low iron conditions (a) promote MT2 induced cleavage of HJV, destabilize TfR2/HFE interaction and reduce BMP6 secretion from the non-parenchymal cells thus reducing BMP signaling and lowering hepcidin expression. High iron conditions (b) increase loading of Tf with iron, stabilize TfR2/HFE interaction and induce BMP6 secretion from non-parenchymal cells. This in turn leads to the formation of BMP6/BMPR/HJV/neogenin/TfR2 /HFE complex which enhances hepcidin expression in hepatocytes. Prepared by M. Matijasic for this project.
PROJECT DETAILS
Project title: Development of novel antibodies (biologics) that will selectively inhibit hepcidin expression in the liver for the Treatment of Anemia of Chronic Disease
Acronym: BMP6Fe3
Project code: 2169
Project type: Research Project
Scientific area: Biomedicine and Health Sciences
Scientific field: Basic Medical Sciences
Principal Investigator (PI): Slobodan Vukicevic, MD, PhD
Institution: University of Zagreb School of Medicine
Project duration in months: 48 (1.7.2017. – 30.6.2021.)
Project funding: This project is funded by the Croatian Science Foundation
Total budget: 1.000.000,00 HRK
SUMMARY OF THE PROJECT
Hepcidin is a 25 amino acid peptide synthesized in the liver and serves as a ligand for ferropoortin, an iron exporter, and thus regulates iron homeostasis. In this project, we aim to develop a therapy for anemia of chronic disease (ACD) associated with an altered iron metabolism based on our discovery that BMP-6 regulates hepcidin synthesis*. We showed that Bmp6-/- mice have decreased hepcidin synthesis in liver and this leads to abundant accumulation of iron in the organism (“hemochromatosis”), suggesting a key role of BMP-6 in hepcidin regulation and iron metabolism. We recently found that ferric (Fe3+) iron induces conformational changes in BMP-6 secondary and tertiary structure thereby exhibiting an high affinity (~4-fold) to BMP co-receptor hemojuvelin (HJV), which results in increased expression of hepcidin and subsequently a decrease of serum iron level (preliminary unpublished results). We propose a new scientific concept to unravel the mechanism by which BMP-6 “senses” iron and develop a novel therapeutic biologics for treating ACD by following objectives: 1) identify physiological forms of circulating BMP-6, 2) produce recombinant human BMP-6, 3) characterize iron specific BMP-6 binding sites, 4) develop high affinity mouse and human antibody to structurally changed BMP-6 in order to prevent the formation of BMP-6-HJV complex in the liver; and pave the path to 5) evaluate newly developed antibodies in vitro and in vivo against anemia associated with inflammation and in a model of chronic kidney disease. Thus, we seek to demonstrate novel concept for understanding the mechanism by which BMP-6 “senses” iron, and utilizes this phenomenon that curtailing Fe3+/BMP-6/HJV mediated hepcidin expression may help to develop the first-in class biologics for ACD.
TEAM MEMBERS
Project scientific leader:
Slobodan Vukicevic, MD, PhD (Laboratory for Mineralized Tissues, University of Zagreb School of Medicine, Zagreb, Croatia)
Project team:
Martina Pauk, PhD (Laboratory for Mineralized Tissues, University of Zagreb School of Medicine, Zagreb, Croatia)
Igor Erjavec, PhD (Laboratory for Mineralized Tissues, University of Zagreb School of Medicine, Zagreb, Croatia)
Hermann Oppermann, MD (Genera Research Ltd., Kalinovica, Croatia)
Irena Popek, (Genera Research Ltd., Kalinovica, Croatia)
Drazen Vikic-Topic, PhD (Rudjer Boskovic Institute, Zagreb, Croatia)